프림(Prim)알고리즘이란
시작 정점에서 출발하여 신장트리 집합을 단계적으로 확장해나가는 방법
프림 알고리즘의 동작
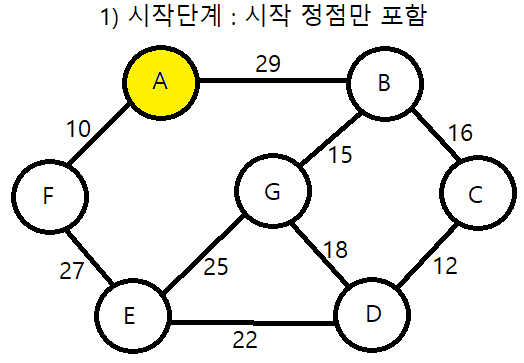
1. 시작 단계에서는 시작 정점만이 MST(최소 비용 신장 트리) 집합에 포함된다.
2. 앞 단계에서 만들어진 MST 집합에 인접한 정점들 중에서 최소 간선으로 연결된 정점을 선택하여 트리를 확장한다.
즉, 가장 낮은 가중치를 먼저 선택한다.
3. 위의 과정을 트리가 (n - 1)개의 간선을 가질때까지 반복한다.
프림 알고리즘의 구체적인 동작과정
프림 알고리즘을 이용하여 MST를 만드는 과정
정점 선택을 기반으로 하는 알고리즘
이전 단계에서 만들어진 신장트리를 확장하는 방법

프림 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도
주 반복문이 정점의 수 n만큼 반복하고, 내부 반복문이 n번 반복
프림 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 O(N^2)이 된다.
Kruskal 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 O(elog₂e) 이므로
그래프 내에 적은 숫자의 간선만을 갖는 '희소그래프(Sparse Graph)'의 경우 Kruskal 알고리즘이 적합하고
그래프에 간선이 많이 존재하는 '밀집그래프(Dense Graph)'의 경우는 prim 알고리즘이 적합하다.
예제코드
강의 C언어 예제코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define NODE_MAX 1001 //노드가 최대 1000개
#define EDGE_MAX 200001 //양방향 간선이므로 100,000개
/*
3 3
1 2 8
1 3 9
2 3 10
을 입력하면 17이 출력된다.
1, 2, 3을 전부 연결할때는 두개간선만 연결하면 되기 때문에
8 + 9가 되어 17이 출력되는것을 확인할 수 있다.
*/
typedef struct {
int cost;
int node;
} Edge; //각 간선의 정보
void swap(Edge* a, Edge* b){ //두개의 간선에 대한 정보를 교체
Edge temp;
temp.cost = a->cost;
temp.node = a->node;
a->cost = b->cost;
a->node = b->node;
b->cost = temp.cost;
b->node = temp.node;
}
typedef struct{
Edge* heap[EDGE_MAX];
int count;
} priorityQueue;
void enQueue(priorityQueue* pq, Edge* edge){
if(pq->count >= EDGE_MAX) return; //총 들어갈 수 있는 간선의 크기를 벗어난 경우
pq->heap[pq->count] = edge; //마지막 인덱스에 새 원소 삽입
int now = pq->count;
int parent = (pq->count - 1) / 2;
//새 원소를 삽입한 이후에 상향식으로 힙을 구성
while(now > 0 && pq->heap[now]->cost < pq->heap[parent]->cost){
swap(pq->heap[now], pq->heap[parent]);
now = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
pq->count++;
}
Edge* deQueue(priorityQueue* pq){
if(pq->count <= 0) return NULL;
Edge* res = pq->heap[0];
pq->count--;
pq->heap[0] = pq->heap[pq->count];
int now = 0, leftChild = 1, rightChild = 2;
int target = now;
//새원소를 추출한 이후에 하향식으로 힙을 구성
while(leftChild < pq->count){
if(pq->heap[target]->cost > pq->heap[leftChild]->cost) target = leftChild;
if(pq->heap[target]->cost > pq->heap[rightChild]->cost && rightChild < pq->count) target = rightChild;
if(target == now) break;
else{
swap(pq->heap[now], pq->heap[target]);
now = target;
leftChild = now * 2 + 1;
rightChild = now * 2 + 2;
}
}
return res;
}
typedef struct Node{
Edge* data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node** adj;
int d[NODE_MAX];
void addNode(Node** target, int index, Edge* edge){
if(target[index] == NULL){
target[index] = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
target[index]->data = edge;
target[index]->next = NULL;
}
else{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = edge;
node->next = target[index];
target[index] = node;
}
}
int main(void){
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); //정점과 간선의 개수 입력
adj = (Node**)malloc(sizeof(Node*) * (n + 1)); //정점의 개수만큼 동적할당으로 연결리스트 생성
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
adj[i] = NULL; //모든 연결리스트는 NULL로 초기화
}
priorityQueue* pq;
pq = (priorityQueue*)malloc(sizeof(priorityQueue)); //우선순위 큐 생성
pq->count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ //모든 간선에 대한 정보 입력
int a, b, c; //c는 가중치. a에서 b까지 가는데 c만큼 소요되는것.
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
Edge* edge1 = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge));
edge1->node = b;
edge1->cost = c;
addNode(adj, a, edge1);
Edge* edge2 = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge));
edge2->node = a;
edge2->cost = c;
addNode(adj, b, edge2);//무방향 그래프
}
//프림 알고리즘 시작
long long res = 0;
Edge* start = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge)); //시작점
start->cost = 0;
start->node = 1;
enQueue(pq, start);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
//신장트리의 경우 총 n개의 정점이 최정적으로 만들어진 신장트리에
//포함되기 때문에 n번만큼 반복
int nextNode = -1, nextCost = INT_MAX;
while(1){
Edge* now = deQueue(pq);
if(now == NULL) break;
nextNode = now->node;
if(!d[nextNode]){
nextCost = now->cost; break;
//방문하지 않은 노드들 중에서 가장 비용이 적은 노드를
//우선순위 큐에서 꺼내준다.
//우선순위큐에는 비용이 적은 노드 순으로 들어가있기 때문에
//과정자체가 방문하지 않은 하나의 노드를 찾겠다는 것.
}
}
if(nextCost == INT_MAX) printf("연결 그래프가 아닙니다.\n");
//못찾았다면 연결그래프가 아닌것이기 때문에 오류메세지를 띄운다.
res += nextCost; //가중치를 누적.
d[nextNode] - 1; //방문처리
Node* cur = adj[nextNode];
while(cur != NULL){
enQueue(pq, cur->data);
cur = cur->next; //인접한 모든 노드를 확인하기 위한 반복문
}
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
system("pause");
}
자바 예제코드
import java.util.*;
public class prim {
static int V, E;
static boolean visit[];
static ArrayList<Edge>[] graph;
static ArrayList<Edge> MST;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt(); // 정점
E = sc.nextInt(); // 간선
graph = new ArrayList[V + 1]; //정점의 연결을 저장할 리스트
visit = new boolean[V + 1]; //방문체크
for(int i = 0; i <= V; i++){
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>(); // 정점의 수 + 1로 초기화
}
MST = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 1; i <= E; i++){
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
int val = sc.nextInt();
graph[u].add(new Edge(u, v, val));
graph[v].add(new Edge(u, v, val));
}
int point = 1; //시작포인트
solve(point);
for(int i = 0; i < MST.size(); i++){
System.out.println(MST.get(i).begin + " " + MST.get(i).end + " " + MST.get(i).value);
//출력.
//begin = 시작, end = 도착, value = 간선
}
}
private static void solve(int P){
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(P); //큐에 시작 정점 add
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //큐가 비어있지 않다면
int now = queue.poll();
visit[now] = true;//큐 순서에 따라 해당하는 인덱스 방문처리
for(Edge e : graph[now]){
if(!visit[e.end]) {//방문하지 않았다면 pq에 add
pq.add(e);
}
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()){//pq가 비어있을때까지 반복
Edge e = pq.poll();
if(!visit[e.end]){//방문하지 않았다면 queue에 넣어주고 방문처리 한 뒤 MST에 add
queue.add(e.end);
visit[e.end] = true;
MST.add(e);
break;
}
}
}
}
public static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int begin;
int end;
int value;
public Edge(int b, int e, int v){
this.begin = b;
this.end = e;
this.value = v;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o){
return this.value - o.value;
}
}
}
레퍼런스
● 패스트캠퍼스 올인원 패키지 - 소프트웨어 베이직
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 다익스트라(Dijkstra) 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.01.20 |
|---|---|
| 크루스칼(Kruskal) 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| 최소신장트리(Minimum Spanning Tree, MST) (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| 해시(Hash) (0) | 2021.01.18 |
| AVL트리 (0) | 2021.01.17 |